|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| asset | ||
| client | ||
| component | ||
| config | ||
| console | ||
| data | ||
| event | ||
| metadata | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .travis.yml | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
| example.yml | ||
| go.mod | ||
| go.sum | ||
| main.go | ||
README.md
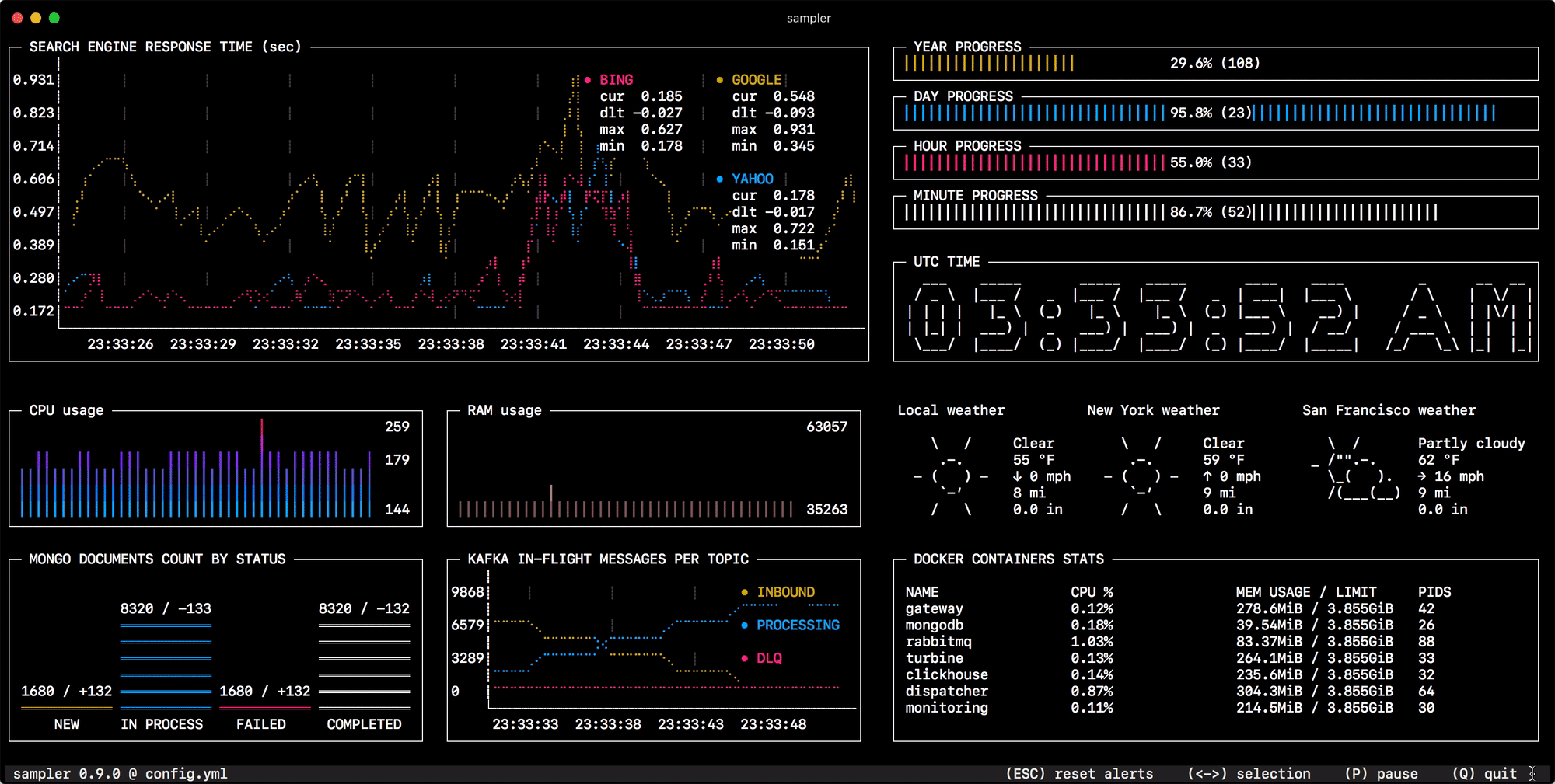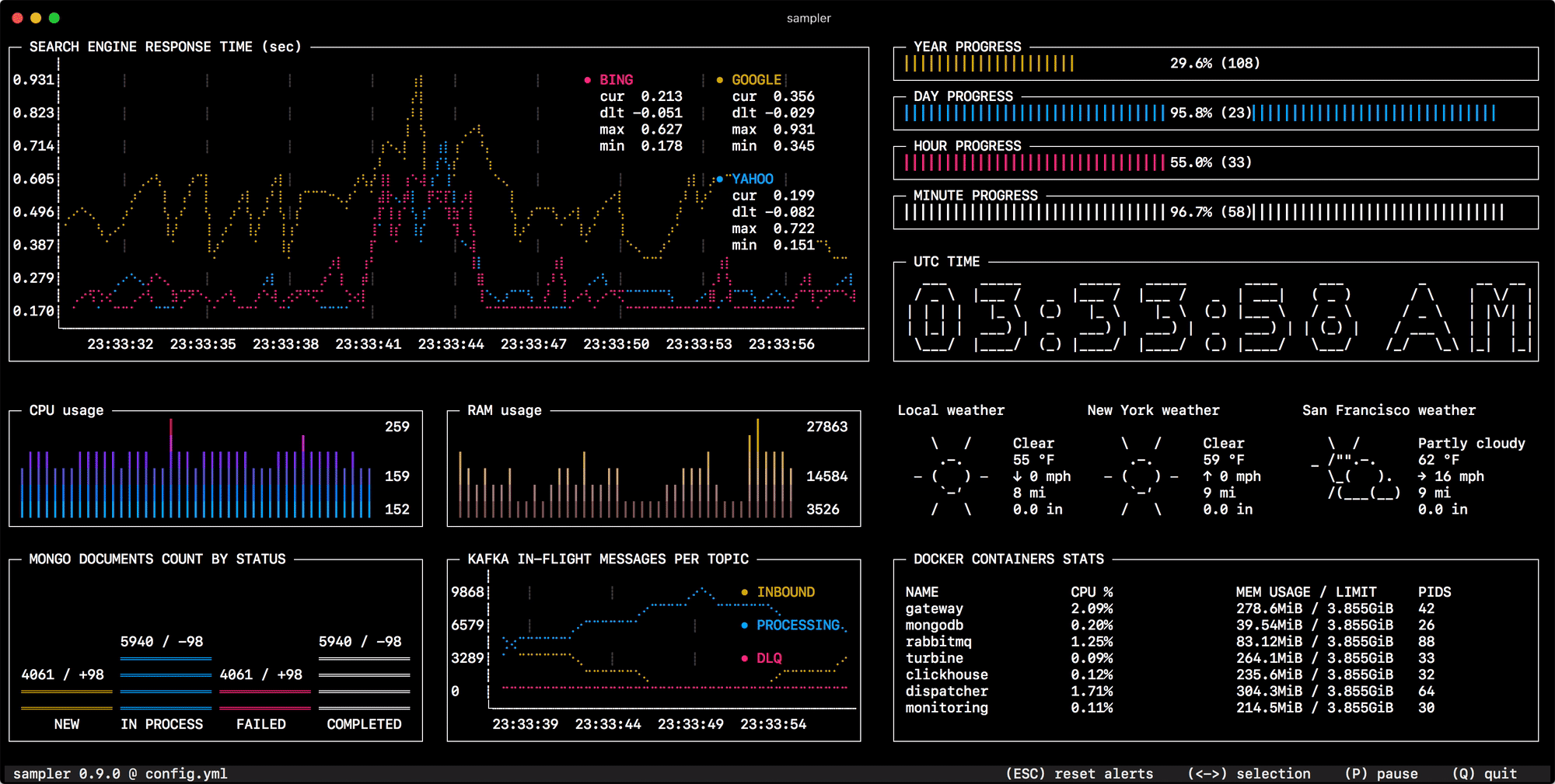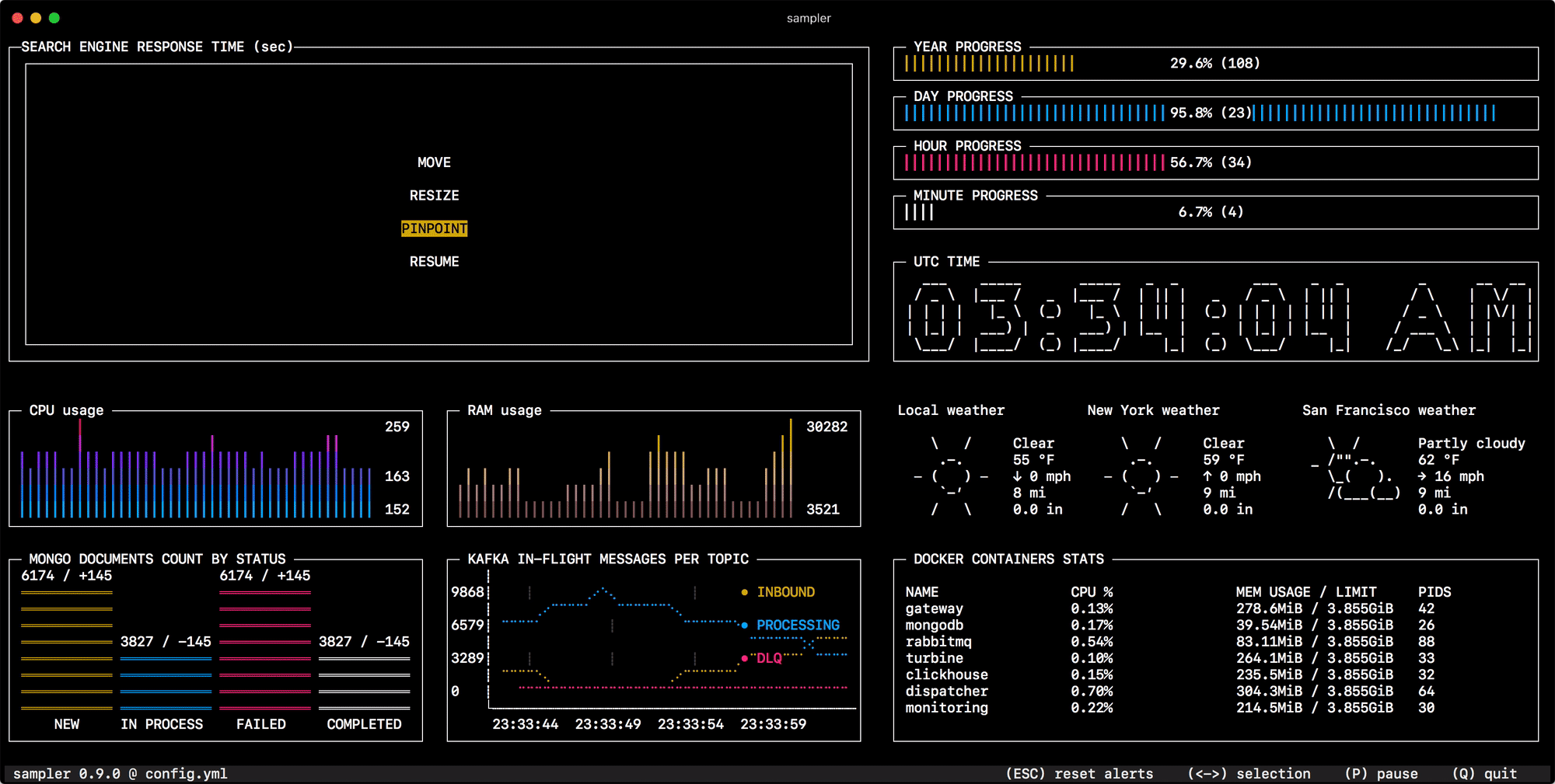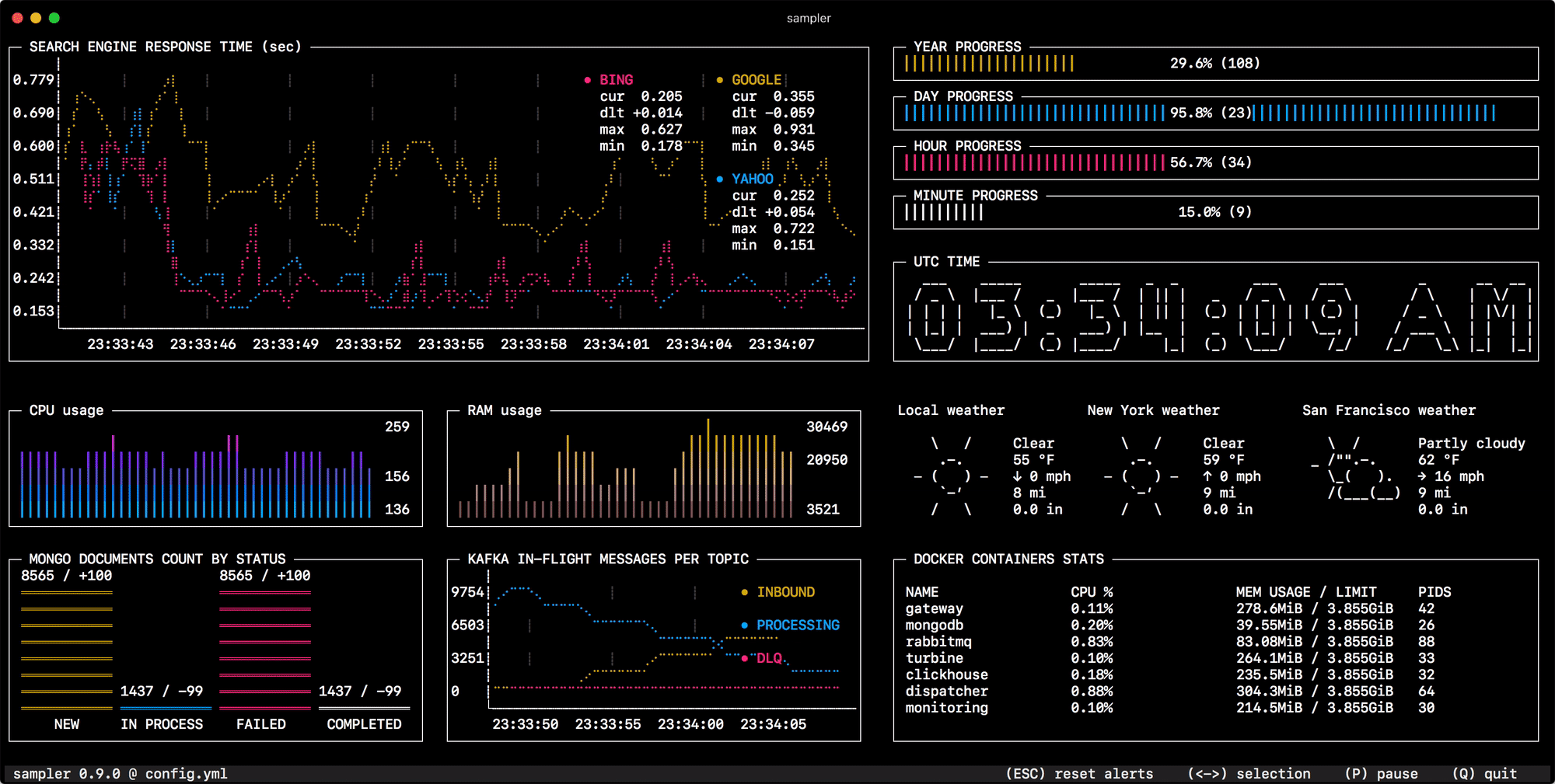
Sampler. Visualization for any shell command.
Sampler is a tool for shell commands execution, visualization and alerting. Configured with a simple YAML file.
Installation
macOS
sudo curl -Lo /usr/local/bin/sampler https://github.com/sqshq/sampler/releases/download/v0.9.1-beta/sampler-0.9.1-darwin-amd64
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/sampler
Linux
sudo wget https://github.com/sqshq/sampler/releases/download/v0.9.1-beta/sampler-0.9.1-linux-amd64 -O /usr/local/bin/sampler
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/sampler
Windows
Usage
You specify shell commands, Sampler executes them with a required rate. The output is used for visualization.
One can sample any dynamic process right from the terminal - observe changes in the database, monitor MQ in-flight messages, trigger deployment process and get notification when it's done.
Using Sampler is basically a 3-step process:
- Define your configuration in a YAML file
- Run
sampler -c config.yml - Adjust components size and location on UI
Contents
Components
The following is a list of configuration examples for each component type, with macOS compatible sampling scripts.
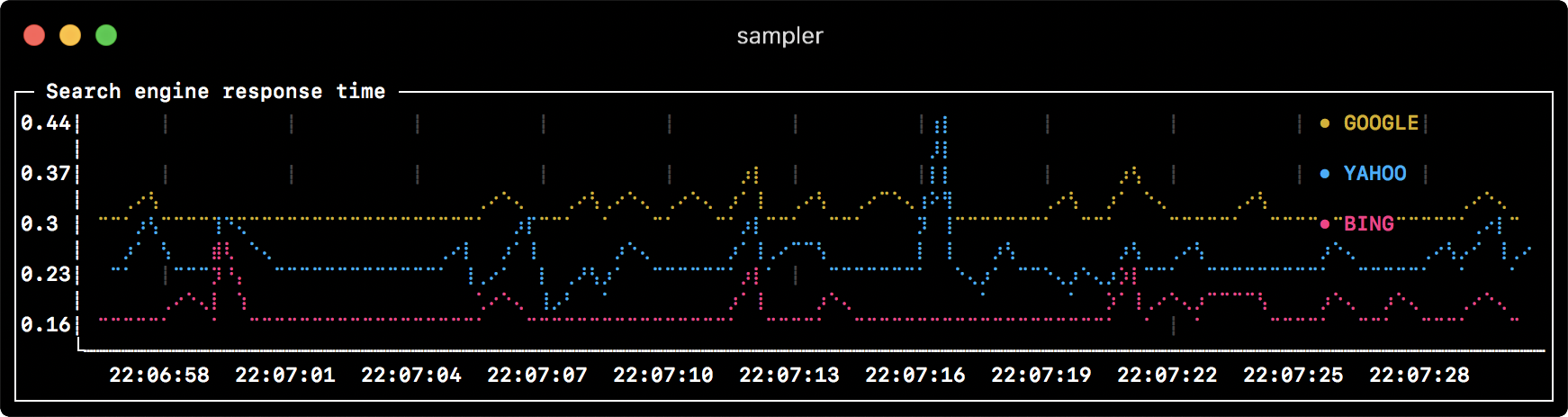
Runchart
runcharts:
- title: Search engine response time
rate-ms: 500 # sampling rate, default = 1000
scale: 2 # number of digits after sample decimal point, default = 1
legend:
enabled: true # enables item labels, default = true
details: false # enables item statistics: cur/min/max/dlt values, default = true
items:
- label: GOOGLE
sample: curl -o /dev/null -s -w '%{time_total}' https://www.google.com
color: 178 # 8-bit color number, default one is chosen from a pre-defined palette
- label: YAHOO
sample: curl -o /dev/null -s -w '%{time_total}' https://search.yahoo.com
- label: BING
sample: curl -o /dev/null -s -w '%{time_total}' https://www.bing.com
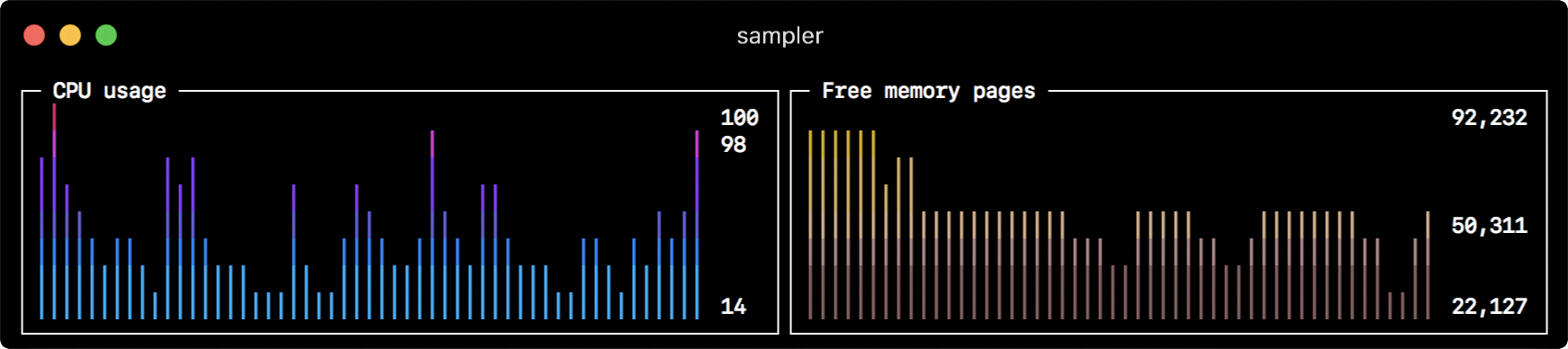
Sparkline
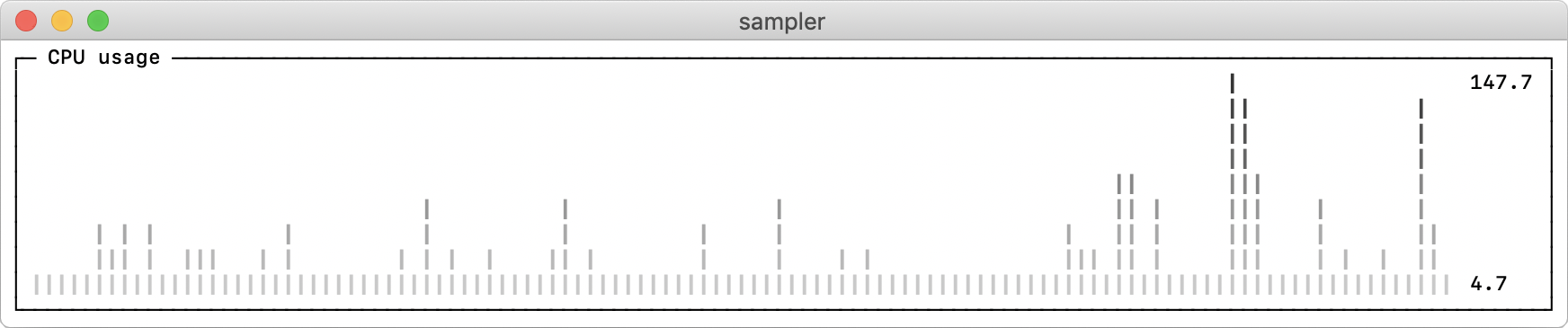
sparklines:
- title: CPU usage
rate-ms: 200
scale: 0
sample: ps -A -o %cpu | awk '{s+=$1} END {print s}'
- title: Free memory pages
rate-ms: 200
scale: 0
sample: memory_pressure | grep 'Pages free' | awk '{print $3}'
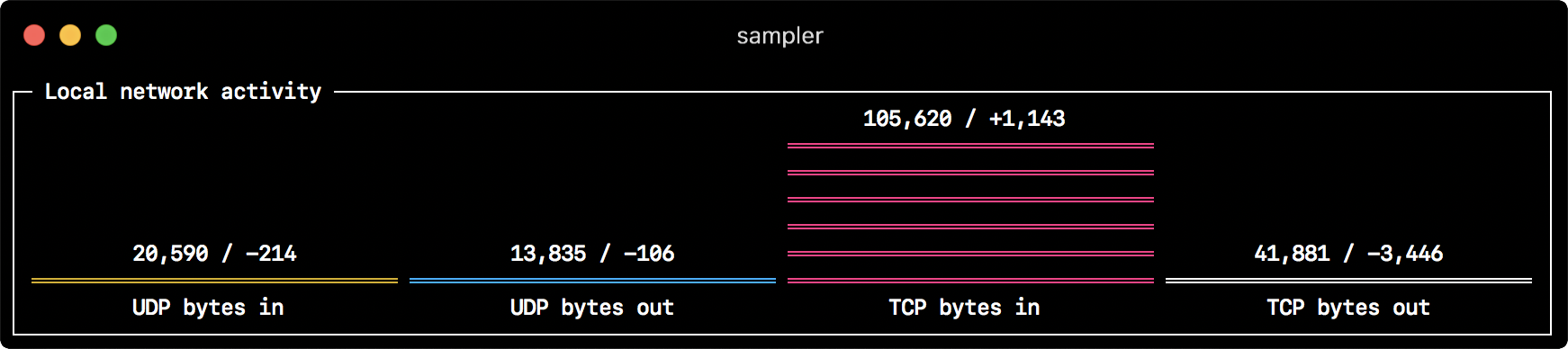
Barchart
barcharts:
- title: Local network activity
rate-ms: 500 # sampling rate, default = 1000
scale: 0 # number of digits after sample decimal point, default = 1
items:
- label: UDP bytes in
sample: nettop -J bytes_in -l 1 -m udp | awk '{sum += $4} END {print sum}'
- label: UDP bytes out
sample: nettop -J bytes_out -l 1 -m udp | awk '{sum += $4} END {print sum}'
- label: TCP bytes in
sample: nettop -J bytes_in -l 1 -m tcp | awk '{sum += $4} END {print sum}'
- label: TCP bytes out
sample: nettop -J bytes_out -l 1 -m tcp | awk '{sum += $4} END {print sum}'
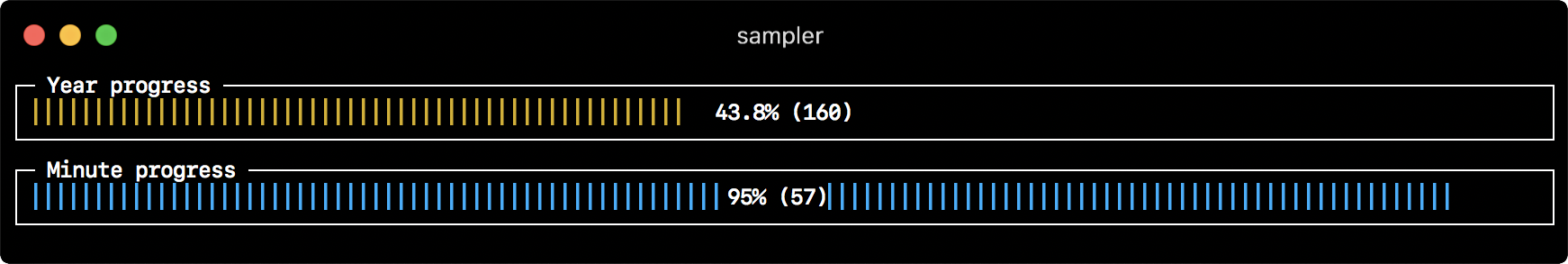
Gauge
gauges:
- title: Minute progress
rate-ms: 500 # sampling rate, default = 1000
scale: 2 # number of digits after sample decimal point, default = 1
percent-only: false # toggle display of the current value, default = false
color: 178 # 8-bit color number, default one is chosen from a pre-defined palette
cur:
sample: date +%S # sample script for current value
max:
sample: echo 60 # sample script for max value
min:
sample: echo 0 # sample script for min value
- title: Year progress
cur:
sample: date +%j
max:
sample: echo 365
min:
sample: echo 0
Textbox
textboxes:
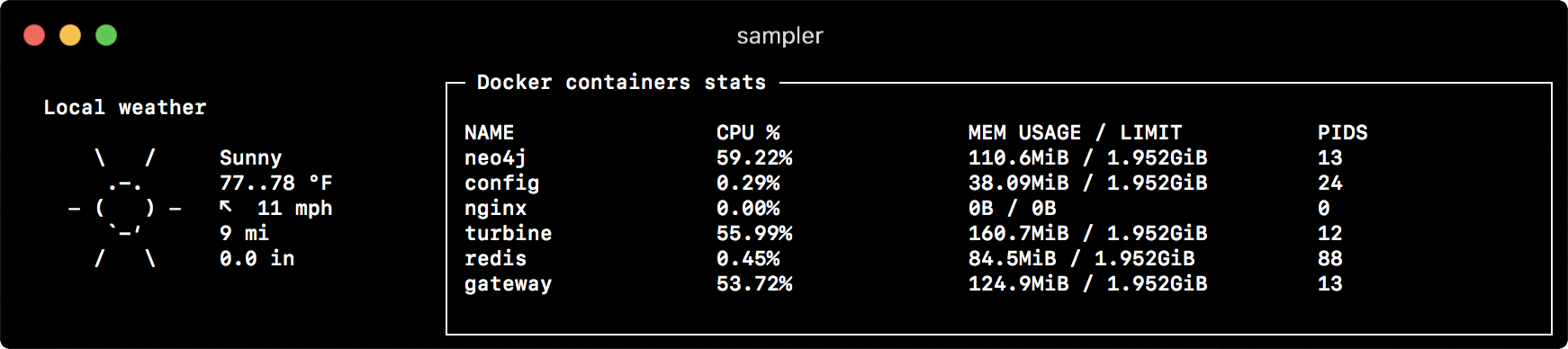
- title: Local weather
rate-ms: 10000 # sampling rate, default = 1000
sample: curl wttr.in?0ATQF
border: false # border around the item, default = true
color: 178 # 8-bit color number, default is white
- title: Docker containers stats
rate-ms: 500
sample: docker stats --no-stream --format "table {{.Name}}\t{{.CPUPerc}}\t{{.MemUsage}}\t{{.PIDs}}"
Asciibox
asciiboxes:
- title: UTC time
rate-ms: 500 # sampling rate, default = 1000
font: 3d # font type, default = 2d
border: false # border around the item, default = true
color: 43 # 8-bit color number, default is white
sample: env TZ=UTC date +%r
Bells and whistles
Triggers
Triggers allow to perform conditional actions, like visual/sound alerts or an arbitrary shell command. The following examples illustrate the concept.
Clock gauge, which shows minute progress and announce current time at the beginning of each minute
gauges:
- title: MINUTE PROGRESS
cur:
sample: date +%S
max:
sample: echo 60
min:
sample: echo 0
triggers:
- title: CLOCK BELL EVERY MINUTE
condition: '[ $label == "cur" ] && [ $cur -eq 0 ] && echo 1 || echo 0' # expects "1" as TRUE indicator
actions:
terminal-bell: true # standard terminal bell, default = false
sound: true # NASA quindar tone, default = false
visual: false # notification with current value on top of the component area, default = false
script: say -v samantha `date +%I:%M%p` # an arbitrary script, which can use $cur, $prev and $label variables
Search engine latency chart, which alerts user when latency exceeds a threshold
runcharts:
- title: SEARCH ENGINE RESPONSE TIME (sec)
items:
- label: GOOGLE
sample: curl -o /dev/null -s -w '%{time_total}' https://www.google.com
triggers:
- title: Latency threshold exceeded
condition: echo "$prev < 0.8 && $cur > 0.8" |bc -l # expects "1" as TRUE indicator
actions:
terminal-bell: true # standard terminal bell, default = false
sound: true # NASA quindar tone, default = false
visual: true # visual notification on top of the component area, default = false
script: 'say alert: ${label} latency exceeded ${cur} second' # an arbitrary script, which can use $cur, $prev and $label variables
Interactive shell support
In addition to the sample command, one can specify init command (executed only once before sampling) and transform command (to post-process sample command output). That covers interactive shell use case, e.g. to establish connection to a database only once, and then perform polling within interactive shell session.
Basic mode
textboxes:
- title: MongoDB polling
rate-ms: 500
init: mongo --quiet --host=localhost test # executes only once to start the interactive session
sample: Date.now(); # executes with a required rate, in scope of the interactive session
transform: echo result = $sample # executes in scope of local session, $sample variable is available for transformation
PTY mode
In some cases intractive shell won't work, because its stdin is not a terminal. We can fool it, using PTY mode:
textboxes:
- title: Neo4j polling
pty: true # enables pseudo-terminal mode, default = false
init: cypher-shell -u neo4j -p pwd --format plain
sample: RETURN rand();
transform: echo "$sample" | tail -n 1
- title: Top on a remote server
pty: true # enables pseudo-terminal mode, default = false
init: ssh -i ~/user.pem ec2-user@1.2.3.4
sample: top
Variables
If the configuration file contains repeated patterns, they can be extracted into the variables section.
Also variables can be specified using -v/--variable flag on startup, and any system environment variables will also be available in the scripts.
variables:
mongoconnection: mongo --quiet --host=localhost test
barcharts:
- title: MongoDB documents by status
items:
- label: IN_PROGRESS
init: $mongoconnection
sample: db.getCollection('events').find({status:'IN_PROGRESS'}).count()
- label: SUCCESS
init: $mongoconnection
sample: db.getCollection('events').find({status:'SUCCESS'}).count()
- label: FAIL
init: $mongoconnection
sample: db.getCollection('events').find({status:'FAIL'}).count()
Color theme
theme: light # default = dark
sparklines:
- title: CPU usage
sample: ps -A -o %cpu | awk '{s+=$1} END {print s}'
Real-world examples
...