|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| asset | ||
| client | ||
| component | ||
| config | ||
| console | ||
| data | ||
| event | ||
| metadata | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .travis.yml | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
| example.yml | ||
| go.mod | ||
| go.sum | ||
| main.go | ||
README.md
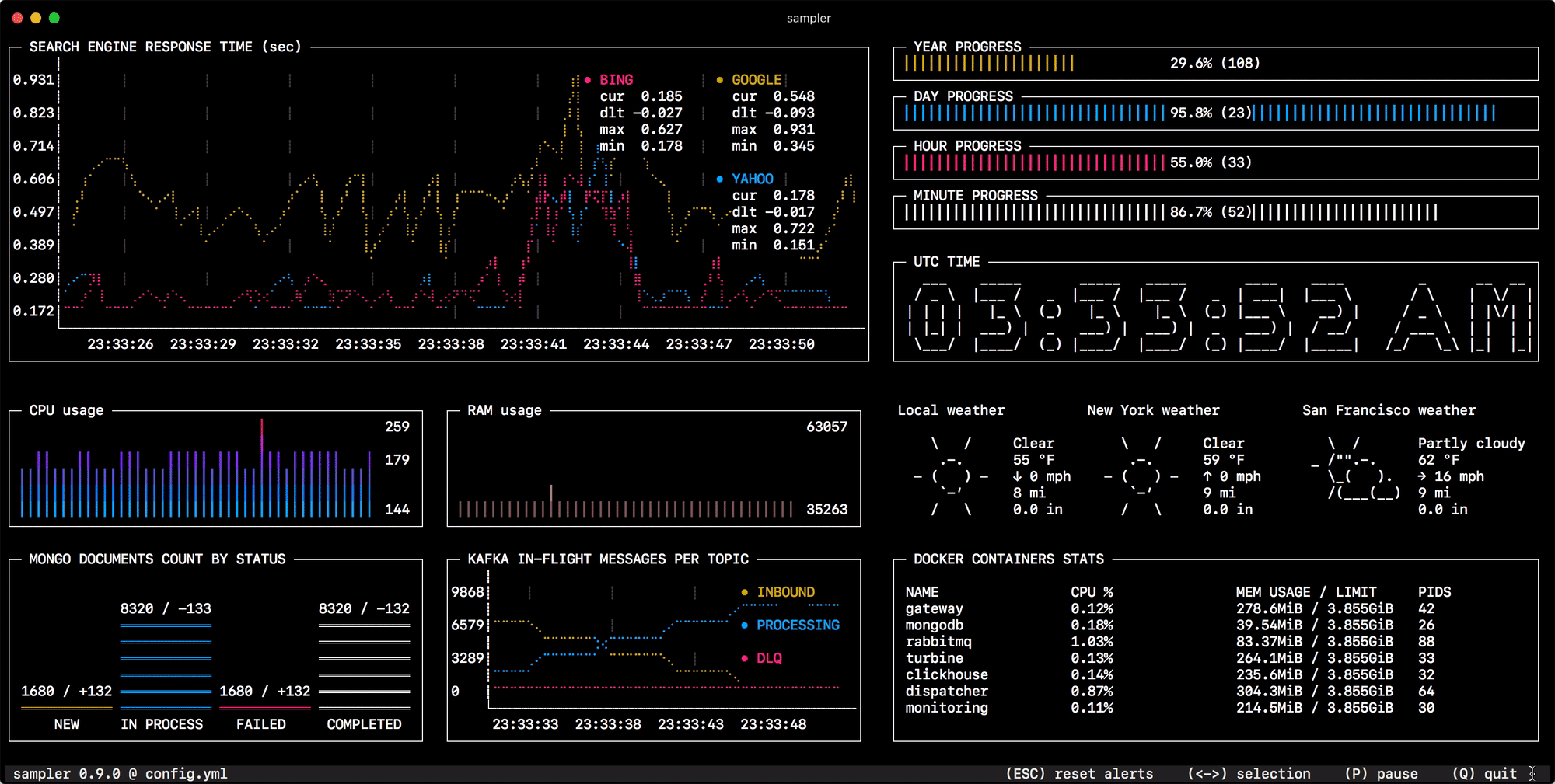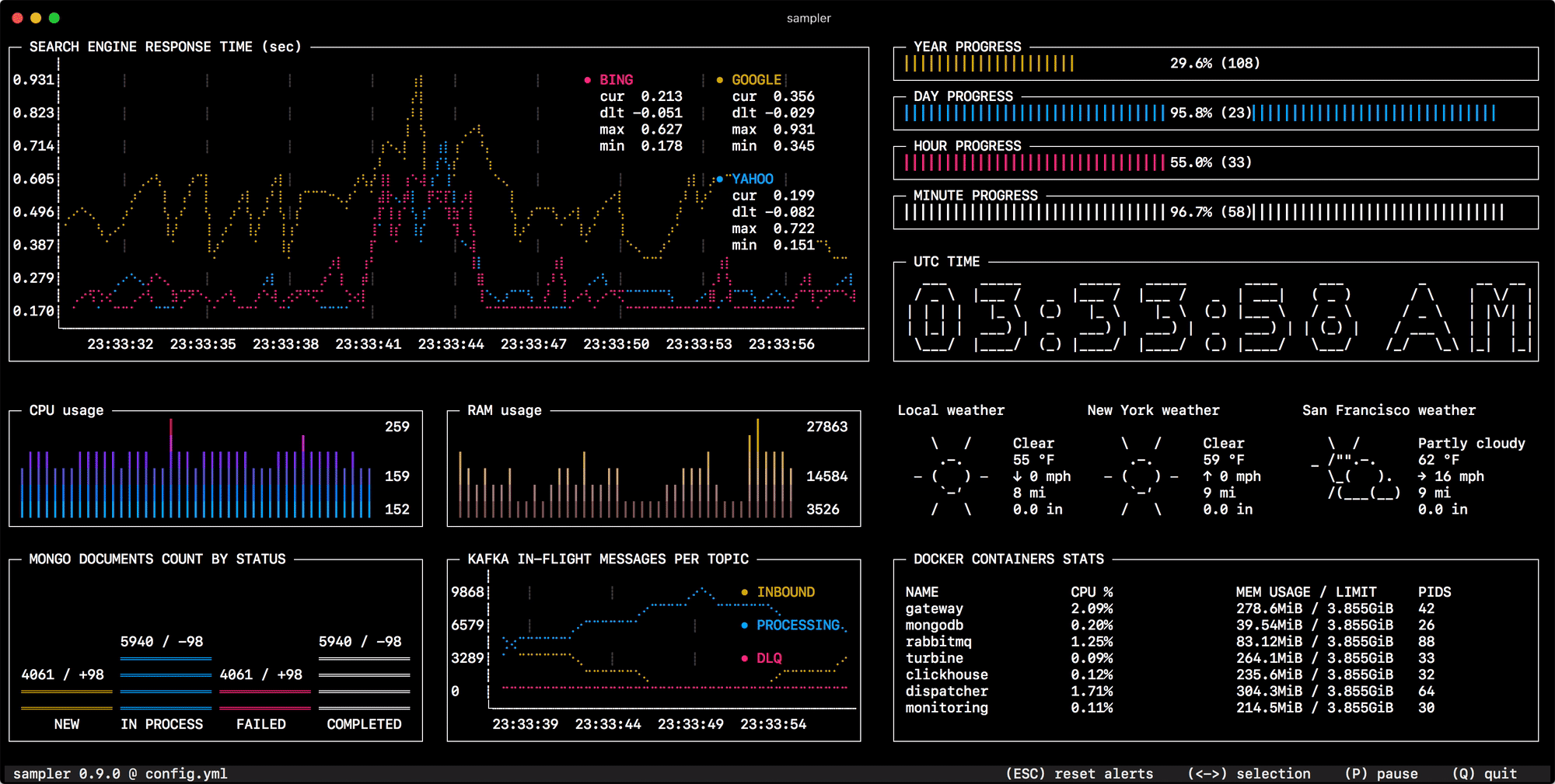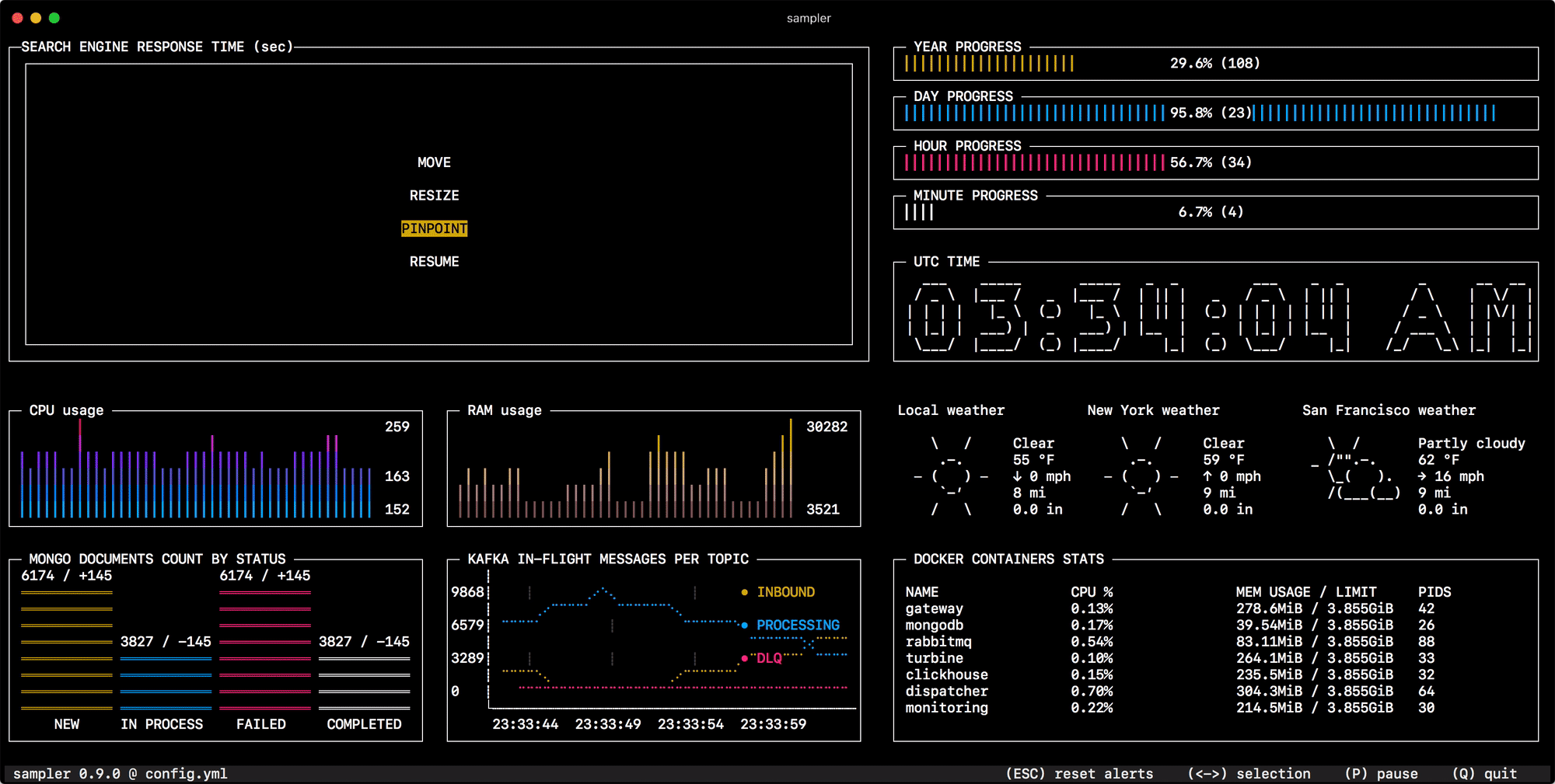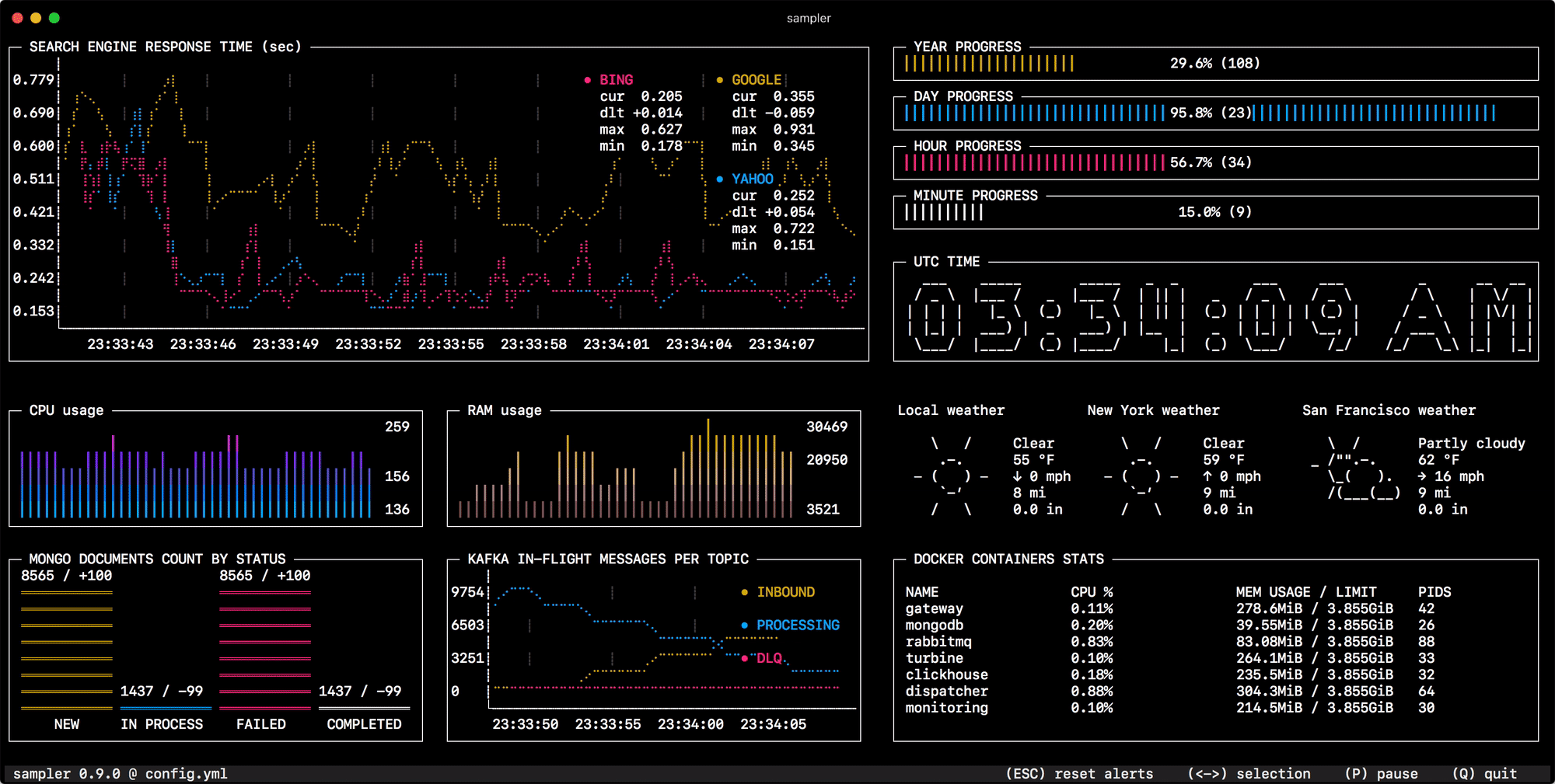
Sampler. Visualization for any shell command.
Sampler is a tool for shell commands execution, visualization and alerting. Configured with a simple YAML file.
Installation
macOS
...
Linux
...
Windows
...
Usage
You specify shell commands, Sampler executes them with a required rate. The output is used for visualization.
One can sample any dynamic process right from the terminal - observe changes in the database, monitor MQ in-flight messages, trigger deployment process and get notification when it's done.
Using Sampler is basically a 3-step process:
- Define your configuration in a YAML file
- Run
sampler -c config.yml - Adjust components size and location on UI
Contents
Components
The following is a list of configuration examples for each component type, with macOS compatible sample scripts.
Runchart
runcharts:
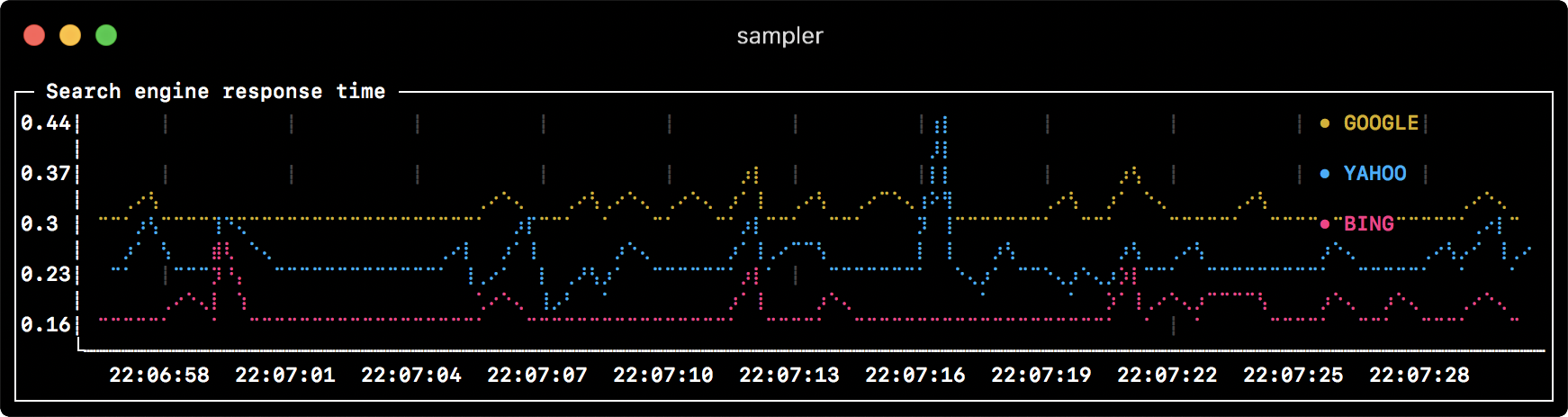
- title: Search engine response time
rate-ms: 500 # sampling rate, default = 1000
scale: 2 # number of digits after sample decimal point, default = 1
legend:
enabled: true # enables item labels, default = true
details: false # enables item statistics: cur/min/max/dlt values, default = true
items:
- label: GOOGLE
sample: curl -o /dev/null -s -w '%{time_total}' https://www.google.com
color: 178 # 8-bit color number, default one is chosen from a pre-defined palette
- label: YAHOO
sample: curl -o /dev/null -s -w '%{time_total}' https://search.yahoo.com
- label: BING
sample: curl -o /dev/null -s -w '%{time_total}' https://www.bing.com
Sparkline
sparklines:
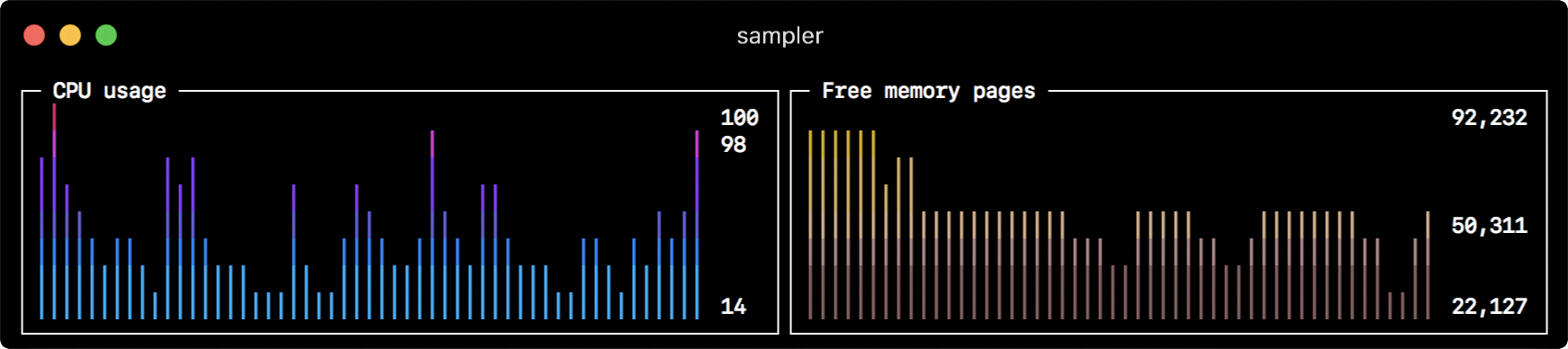
- title: CPU usage
rate-ms: 200
scale: 0
sample: ps -A -o %cpu | awk '{s+=$1} END {print s}'
- title: Free memory pages
rate-ms: 200
scale: 0
sample: memory_pressure | grep 'Pages free' | awk '{print $3}'
Barchart
barcharts:
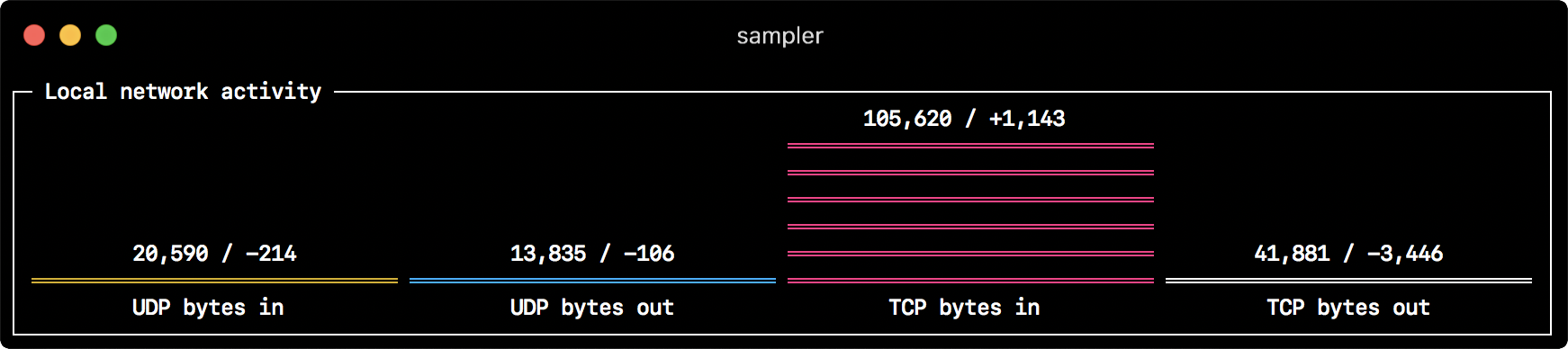
- title: Local network activity
rate-ms: 500 # sampling rate, default = 1000
scale: 0 # number of digits after sample decimal point, default = 1
items:
- label: UDP bytes in
sample: nettop -J bytes_in -l 1 -m udp | awk '{sum += $4} END {print sum}'
- label: UDP bytes out
sample: nettop -J bytes_out -l 1 -m udp | awk '{sum += $4} END {print sum}'
- label: TCP bytes in
sample: nettop -J bytes_in -l 1 -m tcp | awk '{sum += $4} END {print sum}'
- label: TCP bytes out
sample: nettop -J bytes_out -l 1 -m tcp | awk '{sum += $4} END {print sum}'
Gauge
gauges:
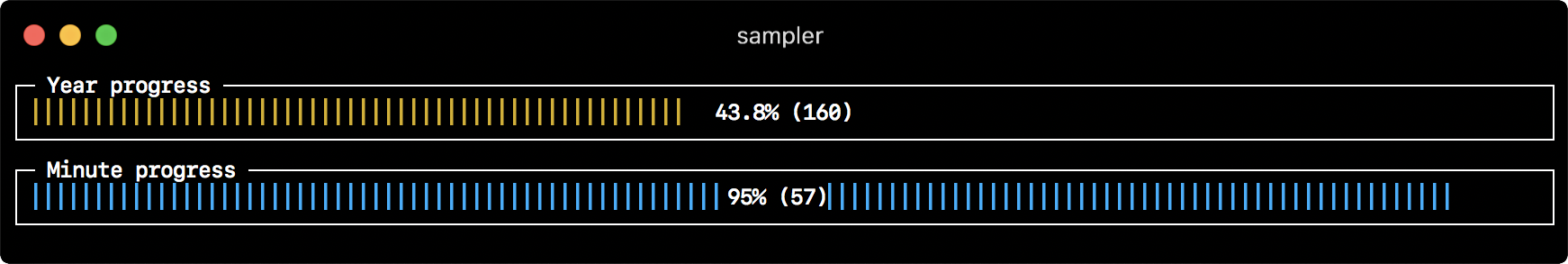
- title: Minute progress
rate-ms: 500 # sampling rate, default = 1000
scale: 2 # number of digits after sample decimal point, default = 1
color: 178 # 8-bit color number, default one is chosen from a pre-defined palette
cur:
sample: date +%S # sample script for current value
max:
sample: echo 60 # sample script for max value
min:
sample: echo 0 # sample script for min value
- title: Year progress
cur:
sample: date +%j
max:
sample: echo 365
min:
sample: echo 0
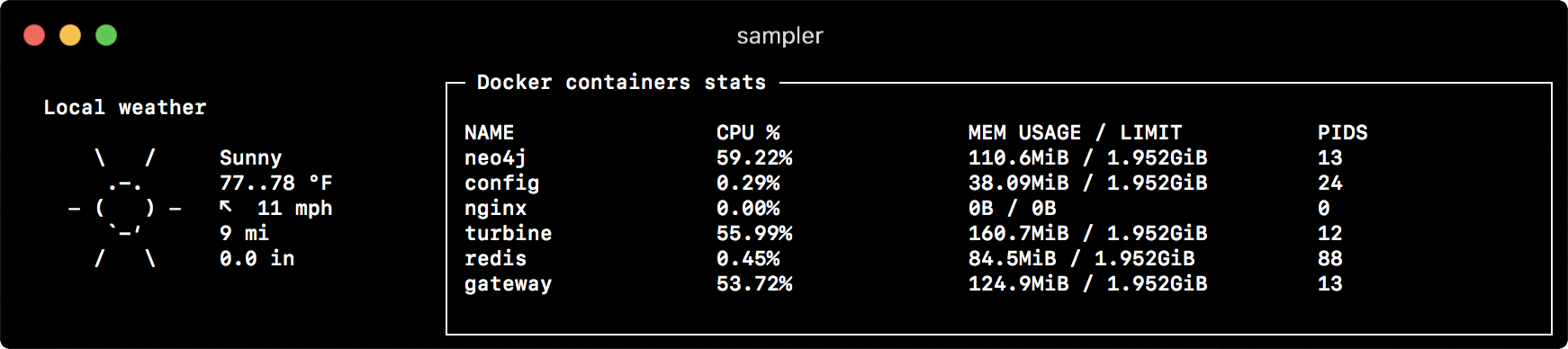
Textbox
textboxes:
- title: Local weather
rate-ms: 10000 # sampling rate, default = 1000
sample: curl wttr.in?0ATQF
border: false # border around the item, default = true
color: 178 # 8-bit color number, default is white
- title: Docker containers stats
rate-ms: 500
sample: docker stats --no-stream --format "table {{.Name}}\t{{.CPUPerc}}\t{{.MemUsage}}\t{{.PIDs}}"
Asciibox
asciiboxes:
- title: UTC time
rate-ms: 500 # sampling rate, default = 1000
font: 3d # font type, default = 2d
border: false # border around the item, default = true
color: 43 # 8-bit color number, default is white
sample: env TZ=UTC date +%r
Bells and whistles
Triggers
Triggers allow to perform conditional actions, like visual/sound alerts or an arbitrary shell command.
Interactive shell support
In addition to the sample command, one can specify init command (executed only once before sampling) and transform command (to post-process sample command output). That covers interactive shell use case, e.g. to establish connection to a database only once, and then perform polling within interactive shell session. MongoDB example: ...
Variables
If the configuration file contains repeated patterns, they can be extracted into the variables section.
Also variables can be specified using -v/--variable flag on startup, and any system environment variables will also be available in the scripts.
Color theme
...
Real-world examples
...